Discover the diversity that drives adaptive immunity
The loci encoding the critical components of the vertebrate immune system are at once highly variable from person to person and hard to sequence. Only HiFi sequencing combines single-molecule accuracy with long read lengths, allowing you to:
- Generate fully phased haplotypes of immunologically important NGS dead zones including the KIR and IGH loci
- Determine HLA haplotypes unambiguously and without imputation
- See the full diversity of the adaptive immune response in action with full-length transcripts and isoforms in targeted, bulk or single cell experiments
Use these applications to explore the immune system with confidence.
Targeted sequencing
Targeted sequencing to generate fully phased HLA haplotypes without imputation with HiFi reads
Profile the BCR repertoire
Profile the BCR repertoire without primer or CDR3 length bias to fully capture somatic hypermutation and resolve both isotype and IgG subclass
RNA sequencing
RNA sequencing to characterize the complete landscape of isoform diversity that distinguishes the many cell types involved in the adaptive immune response
Blog
The HiFi difference – immunology with a FLAIRR
Antibodies are the work horses of the adaptive immune system, identifying and neutralizing foreign objects like bacteria and viruses, and thereby are central to the science of immunology. A new preprint by Dr. Melissa Smith & colleagues from the University of Louisville, entitled FLAIRR-seq: A novel method for single molecule resolution of near full-length immunoglobulin heavy chain repertoires, describes a new gold standard to characterize expressed antibody repertoires.
Spotlight
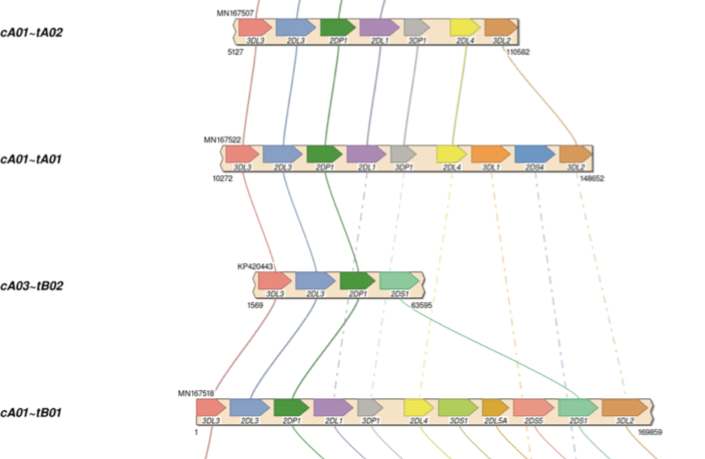
KIR haplotyping with target capture
Using only 18 IDT xGen Lockdown probes, HiFi sequencing, and free software, all diploid human KIR haplotypes were assembled and phased for the first time. Unlike past KIR sequencing methods, it is efficient enough for population-scale studies. The combination of high accuracy and long read lengths were critical to resolving genes that can be up to 98% identical.
Roe, D., et al. (2020) Efficient sequencing, assembly, and annotation of human KIR haplotypes. bioRxiv preprint.
Spotlight
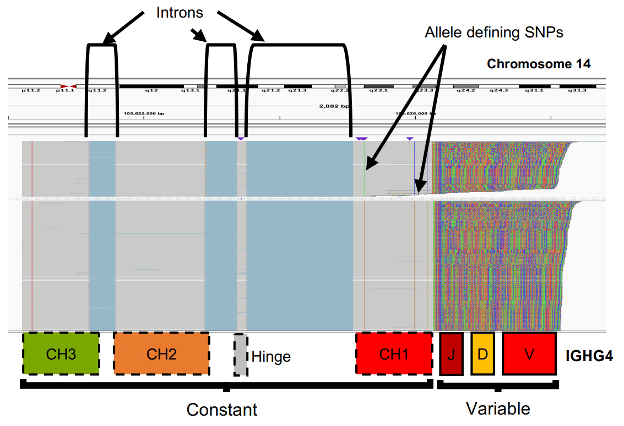
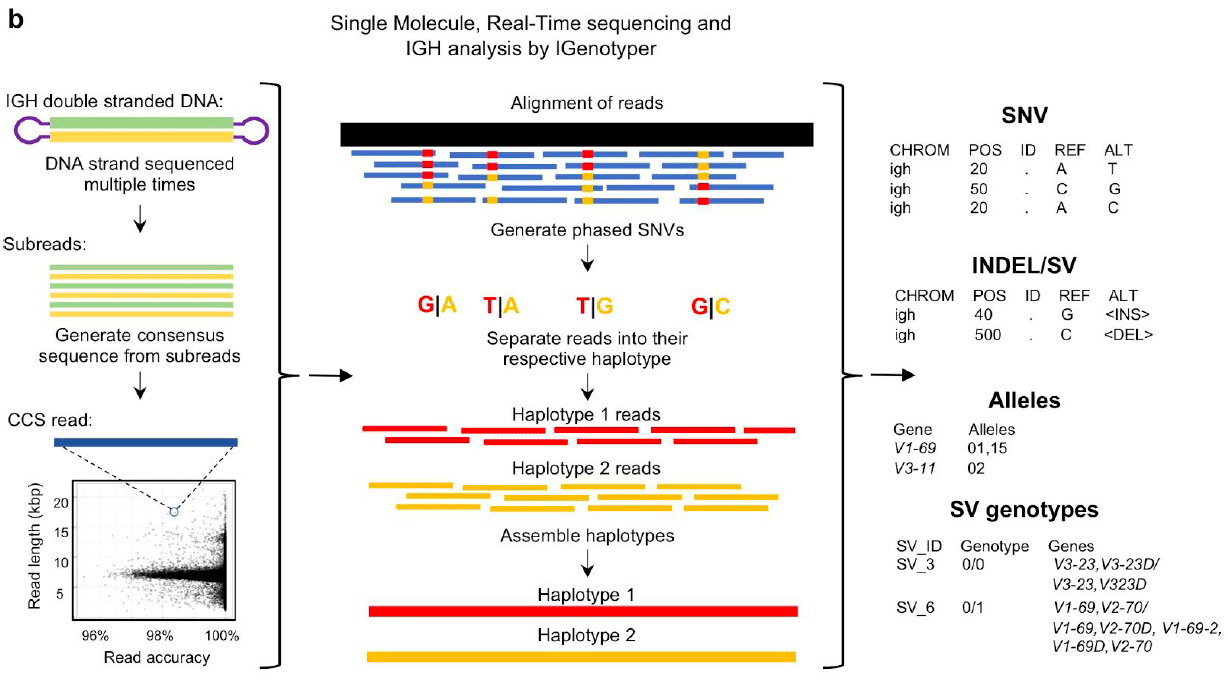
IGH Haplotyping with Target Capture
Target capture enrichment of DNA for IGH sequences followed by HiFi sequencing and analysis with iGenotyper allows locus-wide haplotyping of all IGH variant types for multiple samples in a single run, laying the groundwork to study population-level variation in the antibody response.
Rodriguez, O. L., et al. (2020) A novel framework for characterizing genomic haplotype diversity. bioRxiv preprint.
Blog
In Study, SMRT Sequencing Provides Higher-Resolution HLA Typing Associated with Improved Patient Survival Rates
In a study just published in the Journal of Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, scientists at the Anthony Nolan Research Institute demonstrated that ultra-high-resolution HLA typing performed with SMRT Sequencing identified stronger matches associated with improved survival rates among patients who received hematopoietic cell transplants.